This is a top-notch virtual Presentation Skills Workshop WOMEN…Speak Up!! facilitated by international Public Speaking Coach Jenni Prisk. Madeleine Brecher, Moderator.
The venue was the Commission on the Status of Women in March 2021. It is an engaging 90 minutes-long with excellent examples and Q&A
Archives
Starting a Business
Promotional Techniques
Brochures or flyers — Many desk-top publishing and word-processing software packages can produce highly attractive tri-fold (an 8.5 inch by 11-inch sheet folded in thirds) brochures. Brochures can contain a great deal of information if designed well, and have become a common method of advertising.
Business cards, letterhead and other essentials — From a marketing perspective, do they convey your image? The right message? Be thoughtful about this category, but don’t give it more than its due. Buy in quantity.
Direct mail — Mail sent directly from you to your customers can be highly customized to suit their nature and needs. You may want to build a mailing list of your current and desired customers. Collect addresses from customers by noticing addresses on their checks, asking them to fill out information cards, etc. Keep the list online and up-to-date. Mailing lists can quickly become out-of-date. Notice mailings that get returned to you. This should be used carefully and it can incur substantial cost, you don’t want to inundate your stakeholders with information so make the most of your message.
E-mail messages — These can be wonderful means to getting the word out about your business. Design your e-mail software to include a “signature line” at the end of each of your e-mail messages. Many e-mail software packages will automatically attach this signature line to your e-mail, if you prefer.
Magazines — Magazines ads can get quite expensive. Find out if there’s a magazine that focuses on your particular industry. If there is one, then the magazine can be very useful because it already focuses on your market and potential customers. Consider placing an ad or writing a short article for the magazine. Contact a reporter to introduce yourself. Reporters are often on the look out for new stories and sources from which to collect quotes.
Newsletters — This can be powerful means to conveying the nature of your organization and its services. Consider using a consultant for the initial design and layout. Today’s desktop publishing tools can generate very interesting newsletters quite inexpensively.
Newspapers (major) – Almost everyone reads the local, major newspaper(s). You can get your business in the newspaper by placing ads, writing a letter to the editor or working with a reporter to get a story written about your business. Advertising can get quite expensive. Newspaper are often quite useful in giving advice about what and how to advertise. Know when to advertise — this depends on the buying habits of your customers.
Newspapers (neighborhood) — Ironically, these are often forgotten in lieu of major newspapers, yet the neighborhood newspapers are often closest to the interests of the organization’s stakeholders.
Online discussion groups and chat groups — As with e-mail, you can gain frequent exposure to yourself and your business by participating in online discussion groups and chat groups. Note, however, that many groups have strong groundrules against blatant advertising. When you join a group, always check with the moderator to understand what is appropriate.
Posters and bulletin boards — Posters can be very powerful when placed where your customers will actually notice them. But think of how often you’ve actually noticed posters and bulletin boards yourself. Your best bet is to place the posters on bulletin boards and other places which your customers frequent, and always refresh your posters with new and colorful posters that will appear new to passers by. Note that some businesses and municipalities have regulations about the number of size of posters that can be placed in their areas.
Radio announcements — A major advantage of radio ads is they are usually cheaper than television ads, and many people still listen to the radio, for example, when in their cars. Ads are usually sold on a package basis that considers the number of ads, the length of ads and when they are put on the air. . A major consideration with radio ads is to get them announced at the times that your potential customers are listening to the radio.
Television ads — Many people don’t even consider television ads because of the impression that the ads are very expensive. They are more expensive than most of major forms of advertising. However, with the increasing number of television networks and stations, businesses might find good deals for placing commercials or other forms of advertisements. Television ads usually are priced with similar considerations to radio ads, that is, the number of ads, the length of ads and when they are put on the air.
Web pages — Advertising and promotions on the World Wide Web are almost commonplace. Businesses are developing Web pages sometimes just to appear up-to-date. Using the Web for advertising requires certain equipment and expertise, including getting a computer, getting an Internet service provider, buying (usually renting) a Website name, designing and installing the Website graphics and other functions as needed (for example, an online store for e-commerce), promoting the Website (via various search engines, directories, etc.) and maintaining the Website.
Articles that you write — Is there something in your industry or market about you have a strong impression? Consider writing an article for the local newspaper or a magazine. In your article, use the opportunity to describe what you’re doing to address the issue through use of your business.
Editorials and letters to the editor — Often, program providers are experts at their service and understanding a particular need in the community; newspapers often take strong interest in information about these needs, so staff should regularly offer articles (of about 200 to 900 words) for publication.
Press kits — This kit is handy when working with the media or training employees about working with the media. The kit usually includes information about your business, pictures, information about your products, commentary from happy customers, etc.
Press releases or news alerts — They alert the press to a major event or accomplishment and requesting, e.g., it get included in the newspaper; they explain who, what, where, why and when; some include pictures, quotes, etc. to make it easier for the reporter to develop an announcement or story.
Public service announcements (PSA)s — Many radio and some television stations will provide public service announcements for nonprofit efforts. Usually, these PSAs are free.
Annual reports – Disseminate these to key stakeholders; they’re ripe with information if they include an overview of your year’s activities, accomplishments, challenges and financial status.
Networking – Spread the word to peers, professional organizations and those with whom you interact outside the organizations, e.g., educators, consultants, suppliers, clients, etc.
Novelties — It seems more common to find ads placed on pens and pencils, coffee cups, T-shirts, etc. These can be powerful means of advertising if indeed current and potential customers see the novelties. This condition often implies additional costs to mail novelties, print T-shirts, etc.
Presentations — You’re probably an expert at something. Find ways to give even short presentations, for example, at local seminars, Chamber of Commerce meetings, trade shows, conventions, seminars, etc. It’s amazing that one can send out 500 brochures and be lucky to get 5 people who respond. Yet, you can give a presentation to 30 people and 15 of them will be very interested in staying in touch with you.
Relationships with key stakeholders — Identify at least one representative from each major stakeholder group and take them to lunch once a year. What seem as short, informal exchanges can cultivate powerful relationships of interest and concern.
Special events — These tend to attract attention, and can include, e.g., an open house, granting a special award, announcing a major program or service or campaign, etc.
Special offers — We see these offers all the time. They include, for example, coupons, discounts, sweepstakes, sales, etc.
Social networking — There is an ever evolving variety of online tools that can be used by people and organizations to quickly share a great deal of information at very little cost. Many people are now hearing of some of those tools, e.g., Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn. Experts are asserting that social networking is a must for people and organizations wanting to share information with others — after all, that’s what marketing is all about!
Helpful Glossary of Terms
-
- Blog – A blog (a contraction of the term “Web log”) is a Web site, usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material such as graphics or video. Entries are commonly displayed in reverse-chronological order. “Blog” can also be used as a verb, meaning to maintain or add content to a blog. A blog can be a part of the main site or simply a link to another site that maintains blogs. Having a regularly updated blog on a relevant subject can increase search ratings.
- Browser –A program that allows you to view web pages. Browsers convert
 coded languages like HTML to readable text and images. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome and Safari are all browsers. Browsers, especially Internet Explorer render web pages in their own way. You don’t know what browsers your viewers will be using, so the goal should be to have a good design and user experience even if it looks a bit different in each browser.
coded languages like HTML to readable text and images. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome and Safari are all browsers. Browsers, especially Internet Explorer render web pages in their own way. You don’t know what browsers your viewers will be using, so the goal should be to have a good design and user experience even if it looks a bit different in each browser. - Color Palette – Typically sites are designed with a small number of coordinating colors. These are often based on the existing company
 colors. http://colorschemer.com/ is an example of where to view web safe colors and play with possible combinations.
colors. http://colorschemer.com/ is an example of where to view web safe colors and play with possible combinations. - Content Management – A content management system (CMS) is a way to
 have the client/owner of the website be able to alter and or add content to their site without having to know how to code. Complex content management systems such as Joomla, Drupal or WordPress require that the software be installed on the host first and the site is then built within its templates. Simpler solutions such as Contribute or SnippetMaster can add editable regions to a page after it’s been built.
have the client/owner of the website be able to alter and or add content to their site without having to know how to code. Complex content management systems such as Joomla, Drupal or WordPress require that the software be installed on the host first and the site is then built within its templates. Simpler solutions such as Contribute or SnippetMaster can add editable regions to a page after it’s been built. - CSS – Cascading Style Sheet. Another coding language that allows the style (font, colors, placement of images and text) of a web page to be separated from the content of a page. This allows for faster downloading of pages among other things. CSS and HTML work together.
- Database – A collection of data in tables that relate to each other. A customer list or product inventory are typical uses of databases. Sites can connect to and display data from databases in a variety of ways.
- Domain Name –The address of where the website is located. The domain name it typically purchased and then renewed each year. It does not have to have www at the beginning, but must have a .com, .org etc. at the end. A single site can have more than one domain name pointing to it, or have different domain names pointing to different pages. When domain names are purchased, the vendor provides the DNS address of where the name is and login information to be able to re-direct where that name points to. This is critical information that should be recorded and saved.
- Dynamic – Typically web pages are classified as static or dynamic.
Static pages don’t change content and layout with every request unless a human (web master or programmer) manually updates the page. Dynamic pages adapt their content and/or appearance depending on the end-user’s input or interaction. i.e. Sites can setup links that take you to category listings; this week you see 3 articles, next week you may see 10, but the link hasn’t changed. Or, logging into a bank site and seeing your accounts only. - Ecommerce – The buying and selling of products and services over the internet. Sites can have very simple ecommerce set up by having a “buy now” button from Paypal or Google, or be very complex by having a full blown shopping cart. There are many companies out there offering complex turn-key shopping carts for a monthly fee, but these are for shopping only. Most sites benefit from being informational and having a shopping cart built into it, instead of taking the user to a different site to purchase.
- Flash – An Adobe creative suite program that creates animation. Entire sites can be built in Flash, or just an opening page or header can be in Flash. It is one way to build video and audio into a site. The Flash player must be installed on the user’s local machine for them to see any Flash elements. Current search engines may not be able to read Flash files and the Apple iphone/ipad will not read the files.
- FTP – File Transfer Protocol. When files from a computer need to be transferred to a web site host, this is done through an FTP program. There are many good free programs that can be used (Filezilla, FireFtp, etc.) To do the transfer, an FTP address, login and password are required. (See Hosting)
- Hosting -The computer where the files for the website live is the host. Hosting is typically purchased through a web hosting company. The level of service and control required determine the cost. Domain names and hosting can be purchased from the same company, but it is not required. When hosting is purchased, login information is provided so that files can be uploaded and edited on the site. This is critical information that should be recorded and saved.
- HTML -Hypertext Markup Language. The primary language that web pages are built in.
- IP -Internet Protocol. Every site on the internet, every device on a network is assigned an IP address in a series of numbers. (12.123.450.101) Domain names translate to IP addresses.
- ISP -Internet Service Provider. The company that provides Internet service to your home or office, i.e. Comcast or AT&T.
- MySQL -MySQL is an open source relational database management system.
- Open Source – Software that is often available for free, but more importantly has code that anyone can develop for. Open source often means that forums and other community based ways are the only way to get support. Because of that, open source software is often very flexible and has a lot of extra functionality. Anything from Microsoft is not open source. WordPress is a great example of software that is open source and has many people building plugins and themes for it.
- Photoshop -An Adobe software program to manipulate digital photographs and create art. Many designers will build a mock up of a web page in Photoshop.
- PHP -Hypertext Preprocessor. Server-side HTML embedded scripting language. It provides web developers with a full suite of tools for building dynamic websites. PHP is often used as the link to a MySQL database to display data in a variety of ways.
- Responsive – Responsive web design is an approach where the site is designed to be readable and usable in a wide variety of screen sizes. Ever had to zoom in on a site while on your phone? Or scroll sideways? NOT responsive. In a responsive site the text and navigation will often get bigger, while the columns will get smaller. The point is to make it as human friendly as possible no matter what screen your viewer is on.
- SEO -Search Engine Optimization. A variety of ways to increase the visibility of a site in the search engines like Google or Yahoo. Good updated relevant content, clean coding, hidden (Meta) tags, relevant links to other sites and submissions to DMOZ and other search engines are all basic ways to have a site ‘optimized’. There are many service providers out there that specialize in taking optimization further for a fee.
- Social Media – This refers to the many ways people now have to interact on the Internet. People log on, share content, post comments and feedback, share videos and photos, and participate in a whole host of activities that bring them together – building relationships. More and more of your target market use social market so it is a good way to connect and communicate with them. Then as the theory goes, the friends of your followers get to know what you are up to and the potential for a new customer is born. Small organizations compete with large on a more even playing field. Here are the most popular platforms that have the largest number of users and give you the best opportunity to connect with your target market:

- Social Media Platform – This term refers to the specific website, software, or technology where you carry on your social interactions. There is a wide range of social platforms available, some of which may be appropriate for your organization.
- Social Networking: On these platforms, you can connect with other people of similar interests and likes. Social networking platforms allow you to form or to participate in groups and share and rate information. Business and nonprofit organizations can create a group or specific page so that the people who you serve can engage with you and share your message with their networks. Examples of social networking platforms include Facebook.com and LinkedIn.com.
- Video Sharing: Uploading your videos is a great way to share information in a way that can be more engaging or appropriate than written content. Examples of social video platforms include YouTube.com, Vimeo.com, and Viddler.com.
- Microblogging: These are platforms that allow you to share information with your followers in small blurbs. The most popular microblogging platform is Twitter.com, where all posts are limited to 140 characters but can include links to other websites, images, or videos.
- Blogs: With a blog, you can post written or video content for others to read, view, and comment upon. There can be a single author on a blog or many. There are many free and paid blogging platforms, with the most popular being WordPress.com and Blogger.com. Others include Tumblr.com, Weebly.com, and SquareSpace.com.
- Social News: These are platforms that allow you to share news or other outside articles with the community. Typically, social news platforms allow members of the community to vote or rate content so that the highest voted content is prominently displayed. You can expose more people to your business or mission by sharing valuable content and building up a community of people who follow you. Examples of popular social news sites include Digg.com and Reddit.com.
- Social Bookmarking: These are platforms that allow you to save, share, and organize websites or other Internet-based resources. Most social bookmarking sites allow you and others to tag and search the bookmarked content. Like social news sites, you can leverage social bookmarking to engage with more potential customers by bookmarking important or valuable websites that are related to your business or mission. Examples of social bookmarking sites include Delicious.com and StumbleUpon.com.
- Photo Sharing: You can create an account and upload your photos, which you can present individually or in digital albums. Social photo-sharing platforms include Flickr.com and PhotoBucket.com. You can also share photos on social networking sites like Facebook and Google+.
- Content Curation: These are platforms that allow you to pull together and organize content from other websites. One of the most popular sites, Pinterest, allows you to create virtual pin boards that organize content around a certain topic. You can then “pin” images and videos to those boards and share the pinned content with other followers.
- Wikis: On these collaborative platforms, users contribute articles to create fast-growing information sites—kind of like an encyclopedia, but one in which users create the content. The best and most well- known example of a wiki is Wikipedia.com.
-
- Template or Theme – A master page used to produce web pages. Sites can be designed with one or many master templates, i.e. the home page may have a different layout from the following pages. A site can also be designed with several ‘skins’ to reflect a special event or season. There are many pre-designed templates available for the major content management systems like WordPress & Joomla.
How Much Does a Small Business Website Cost?
Understanding the three basic requirements for starting a website.
- Domain name – This is the address where your website will be found on the Web. The best domain name is one that uses the company’s name in the URL. But sometimes that can be hard to get, if you haven’t already registered it. If you can’t get your company name, then consider something catchy or memorable that your customers can associate with you. It needs to be relevant to your company (containing your company’s name), easily remembered, and easy to spell. Once you’ve committed to a name, you’ll want to stick with it. Remember that it should be something that you like and can live with for a long time, as there’s a possibility that people will start remembering your domain name before they remember your real company name.
Cost: $20/year or less - Web Hosting/Internet Service Provider – Your ISP simply provides access to the internet. If you want a website of your own, you will need to effectively “rent” the space for it on a hosting company’s server. Deciding where you’re going to put your website is important. You want flexibility, excellent support, great reputation, reasonable cost. Once you have both a domain and hosting account, you will need to point the domain to your host’s nameservers, to connect the domain name to the server. When you signed up, your hosting provider should have sent you the names of the nameservers. They look something like nameserver.com and ns2.nameserver.com.
Cost: 150/ year or less for basic service - Someone to Build the Website and Maintain it.
First determine what you need. A graphic designer focuses on creating images – so they can help if you need a logo and a particular web template that is unique to you; but they may need to work with a web designer for the finished product. A web developer/coder can build any type of website you can think of, but they may need to work with a designer to make it look the way you want it. A web designer is someone who can translate your vision into an actual, tangible website – the layout, content editing, images, graphics – using WordPress templates or code-free, drag and drop website builders like Weebly – then teach you how to keep it updated.
Cost: $250 (basic WordPress, with you providing content) to $5,000 (relying totally on experts).
Knight@Work clients:
On average, the following figures can be applied to estimating the cost of a website. When we say “small business website” we are talking about an informational website consisting of approximately 5 pages with some basic content management and social media widgets.
Domain Name – $20/year
Hosting – $150 /year
Web Planning, Design and Development of basic Word Press site: $400 *
* Discount offered for a reduced number of pages and full content provided electronically
Estimate includes instructions and documentation explaining how to maintain and edit site content and 12 months of support.
Addons are an extra $25/hour: Additional pages, Content writing, Blog set up, Photo Gallery, Customized Forms, etc.
Website Maintenance after the first year – $25/hour or $150/year
Marketing/Promotional Support – $25/hour
A simple agreement of work and costs will be provided before work is begun.
Clients must pay upfront for Domain name and Hosting, and 1/2 the agreed upon website fee. The balance is due when site is near completion.
Getting Started with a Website
When you are ready to start a website, complete the following exercise…then we can talk.
![]() Step by Step Basics for Planning an Effective Website
Step by Step Basics for Planning an Effective Website
Website name:
Owner:
Address:
Phone:
Email:
- Provide a brief overview of your organization. What do you do or produce?
- What is the purpose of this site? You need to have a clear goal for your website including the business problem you’re trying to solve. Below are a few examples to choose from; add any additional goals. Check all that apply; add any additional goals.
- Explain your products and services
- Bring in new clients to your business
- Provide your customers with information on a certain subject
- Deliver news or calendar of events
- Create a blog that addresses specific topics or interests
- Allow clients to pay online and to request service
- Provide support for current clients
- Do you have a timeframe or deadline to get this site online?
(If you have a specific deadline, please state why.)
Generally, development takes 2-3 weeks once content and pictures are finalized. - How much are you willing to spend? Web design companies work within a set of given constraints. Your budget is one of them. If you know how much you can spend on a web design project, this information will make it much easier to recommend an approach and will save us both a considerable amount of time.
- Target market
Who will visit this site? Describe your potential clients. Young, old, demographics etc. - Why do you believe these potential clients should do business with you rather than with a competitor? What sets you apart?
- What call to action (CTA) should the potential clients perform when visiting your site? Check all that apply; add any additional goals.
- Call you
- Fill out a contact form /email
- Fill out some other form (explain)
- Sign up for your mailing list
- Search for information
- Purchase a product(s)
- Other:
- Sections/Pages
Review your purpose (#2) and make a list of all the sections/pages you think that you’ll need. (Review websites in similar markets to get ideas if you need a starting place.)
| Page | Content Notes |
| Home | |
| Contact Us | |
| Our Services | |
| About Us | |
Or create a site map:
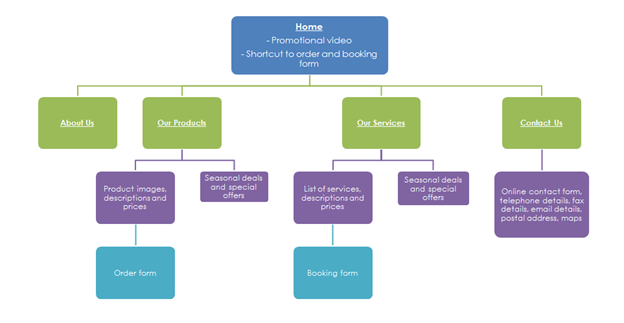
- Written content and images/photographs.
Do you have the written content and images/photographs prepared for these pages? If not, will you need copywriting and photography services?
(Please note that before any real design work or site construction can begin, an outline of the content and preferably all of the content will be needed.)
- Design elements
When people come to your new site for the first time, how do you want them to feel about your organization? Are there specific colors, logo, fonts etc. that should be incorporated? If you do not already have a logo, are you going to need one designed? Is there a specific look and feel that you have in mind? - Websites of your closest competition
Please include at least 3 links of sites of your competition. What do you like and don’t like about them? What would you like to differently or better?
- Websites that you like
Along with putting down the site address, please comment on what you like about each site, i.e. the look and feel, functionality, colors etc. These do not have to have anything to do with your business, but they could have features you like. Please include at least 3 examples.
(Caution A website should focus more on what your customers like and what they will respond to than on your personal preference, so don’t get lost in your own personal style.)
- Marketing the Site
How do people find out about your business right now? Have you thought about how you’re going to market this site?
Do you have any social network accounts setup? (Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram, etc.) Do you want links to those accounts on your site?
Do you have a mail service account? (Constant Contact, MailChimp etc.) Will you want to build your mailing list and use it for advertising & newsletters?
Will you want printed materials (business cards, catalog, etc.) produced as well?
If someone were searching for your product/service, what types of search terms (single words or phrases) might they use? Please list all the possible search terms you can think of.
- Maintenance
The best sites on the Web change frequently and are kept up-to-date. If you’re planning a website for your business you should factor in the cost of having at least one person who adds new content at least weekly and fixes problems as they are found.
Will there be sections that need regular updating? Which ones? Would you like to be able to do most of the updating yourself?
If you’re planning on writing a blog do you already have several things written? Do you already write on a regular basis?
Are there any features/pages that you don’t need now but may want in the future? Please be as specific and future thinking as possible.
Yes, this is a lot of work for you. And it is all necessary.
It is part of the collaborative process of developing a website; it is critical work for creating /designing the finished product. And, the upfront work will pay off for you in keeping the cost and timing for this project as cost-effective as possible.
Just what is Marketing Communications?
Marketing Communications might be defined as the process of promoting the exchange of something of value (your product or service) for something you need (such as money or support), by building on your brand and motivating people to respond.
My expertise for this work covers four primary areas:
- effective writing – the ability to craft key messages for your target audience;
- design – the knack for creating a look to match the image you want to convey;
- technology – the skills needed to build websites, do research, navigate social media;
- savvy – the capability to assist with a wide range of promotional possibilities.
As a Marketing Communications COACH, I add additional value to our relationship. I provide your organization with ongoing support and advice to maximize your marketing efforts.
I spend a lot of time thinking about and working with my clients. I don’t work with just anyone and I’m sure you don’t either. So give me a call and let’s see if we’re a good fit.
If you are interested in creating or updating a website, here is an exercise that will get you started. If you need help with web-related terminology, check out this glossary.

